As modern manufacturing continues to evolve, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines have become an essential part of the industry. These machines play a critical role in automating tasks with extreme precision, allowing manufacturers to produce complex parts with high efficiency. However, many people are curious about how these machines operate and, specifically, what language they use to follow commands.
Understanding the language used by CNC machines is crucial for manufacturers looking to optimize their processes. In this article, we at HIRUNG will guide you through the world of CNC programming languages, highlight their importance, and explain why G-code remains the gold standard in the industry. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned machinist, you’ll find valuable insights to improve your CNC machining capabilities.
What is CNC Programming?
At its core, CNC programming is the process of writing instructions that a CNC machine uses to cut, shape, or finish a workpiece. These instructions tell the machine what movements to make, how fast to move, and when to engage different tools. By using precise code, manufacturers can achieve incredible accuracy, which is especially important when producing high-quality parts.
CNC programming is crucial because it ensures the consistency and repeatability of parts—something that would be difficult to achieve with manual machining. In short, mastering CNC programming is key to unlocking the full potential of your CNC machinery, allowing you to maximize productivity and minimize errors.
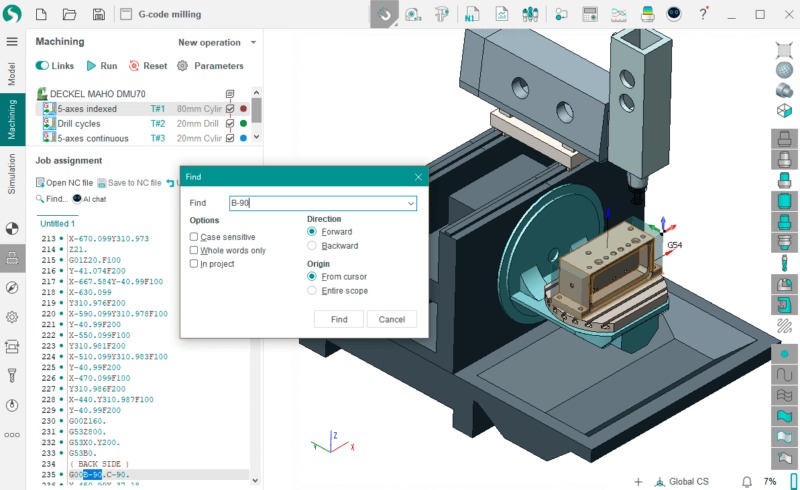
Types of CNC Programming Languages
When it comes to CNC programming, there are several languages that machines can understand, each with its unique purpose. Below, we break down the most commonly used languages:
1. G-Code (the Standard Language)
G-code is the most widely used CNC programming language and has been the industry standard for decades. Developed in the early days of numerical control, G-code remains popular due to its simplicity and compatibility with nearly all CNC machines.
Key Features of G-Code:
- Precise Control: It allows operators to control the movement of the cutting tool, specifying coordinates, feed rates, and spindle speeds.
- Widely Supported: G-code is compatible with various CNC machines, making it the go-to language for manufacturers worldwide.
- Flexible: Whether you’re machining metal, plastic, or composite materials, G-code can be adapted to different processes.
Common G-Code Commands:
- G00: Rapid positioning
- G01: Linear interpolation (used for straight cuts)
- G02/G03: Circular interpolation for clockwise and counterclockwise arcs
- M03/M05: Spindle control (on/off)
These commands form the building blocks of most CNC programs, allowing machinists to produce intricate parts efficiently.
2. M-Code (Machine Code)
While G-code handles most of the movement and tool-related commands, M-code focuses on auxiliary functions. It controls operations like turning on the coolant, stopping the spindle, or engaging a tool change.
Examples of M-Code:
- M08: Coolant on
- M30: End of program and reset
Understanding the distinction between G-code and M-code is essential for efficiently operating CNC machines and achieving the best results.
Why G-Code Remains the Standard Language
Despite the rise of new technologies and programming methods, G-code continues to be the most widely used language in CNC machining. Why is that? Here are a few reasons:
- Simplicity: G-code is straightforward, making it easier for machinists to learn and implement.
- Universal Compatibility: Most CNC machines, regardless of their make or model, can understand G-code, making it a versatile option for manufacturers.
- Proven Reliability: Decades of usage have proven G-code to be robust and efficient for precision manufacturing.
How to Learn CNC Programming
If you’re new to the world of CNC programming, learning G-code can be a game-changer for your machining skills. Here are some practical steps to get started:
- Start with Online Resources: There are plenty of free tutorials, forums, and videos available online to get you familiar with the basics.
- Enroll in Specialized Courses: For those looking to advance quickly, consider taking certification courses in CNC programming.
- Practice with Simulation Software: Many software tools allow you to simulate G-code on your computer, letting you practice without risking damage to your machine.
- Hands-On Experience: The best way to learn is by doing. Start with simple projects to build confidence before tackling more complex tasks.

The Future of CNC Programming Languages
While G-code remains the dominant language, there are trends that could shape the future of CNC programming:
- CAM Software Integration: With the increasing use of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, many tasks that once required manual coding can now be automated, allowing for more efficient workflows.
- Conversational Programming: Some modern CNC machines support conversational programming interfaces, which are more intuitive and user-friendly.
- AI and Automation: As AI technologies advance, CNC programming may shift towards more automated and adaptive systems, reducing the need for manual intervention while still relying on G-code as the underlying structure.
Why Choose HIRUNG CNC Machine Tools
At HIRUNG, we understand the critical role that precise CNC programming plays in the manufacturing process. Since expanding into international markets in 2015, we have been committed to producing high-end CNC machine tools that meet the highest standards of quality.
Here’s why HIRUNG stands out:
- Expertise in Precision: We focus exclusively on Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs), ensuring that each machine we manufacture meets rigorous quality standards.
- Global Reach: Over the past nine years, we have exported our products to 33 countries and regions, establishing ourselves as a trusted provider of CNC solutions.
- Continuous Improvement: Our team is dedicated to constantly enhancing our products to ensure maximum reliability, precision, and performance.
If you’re looking for a partner that understands the complexities of CNC machining and can deliver the high-quality equipment you need, HIRUNG is here to help. Contact us today to learn more about our CNC solutions and how we can support your manufacturing needs.
Conclusion
CNC machines are at the heart of modern manufacturing, and understanding the language they use—primarily G-code—can significantly enhance your production capabilities. As the industry evolves, mastering CNC programming remains a valuable skill, whether you’re a beginner looking to learn the ropes or an experienced machinist aiming to optimize your processes.
HIRUNG is committed to helping manufacturers achieve precision and efficiency in their operations. By leveraging our high-quality CNC machines and decades of expertise, you can take your machining processes to the next level. Reach out to us for more information on how we can support your business in achieving its manufacturing goals.